The assets borrowed could include cash, consumer goods, or large assets such as a vehicle or building. The interest rate is the percent of principal charged by the lender for the use of its money. An interest rate is the amount of interest due per perio as a proportion of the amount lent, deposited or borrowed (called the principal sum). It is defined as the proportion of an amount loaned which a lender charges as interest to the borrower, normally expressed as an annual percentage. What is an interest rate ? An interest rate is defined as the proportion of an amount loaned which a lender charges as interest to the borrower, normally expressed as an annual percentage.
It is the rate a bank or other lender charges to borrow its money, or the rate a bank pays its savers for keeping money in an account. This is why economists are so obsessed with interest rates. Jan Explaining the different types of interest - saving rates, bond rates, Central Bank base rates and the definition of real interest rates.
In a loan structure whatsoever, the interest rate is the difference (in percentage) . On the contrary, by cutting interest rates , a central bank might be seeking to boost economic activity by fostering credit expansion or currency depreciation in . Imagine you have a £130mortgage with an interest rate of 2. Dec Who Determines Interest Rates ? Interest rates are based on three key financial and economic factors, as follows: The Federal Reserve. But do you know how they. Lesson summary: nominal vs. How Do Interest Rates.
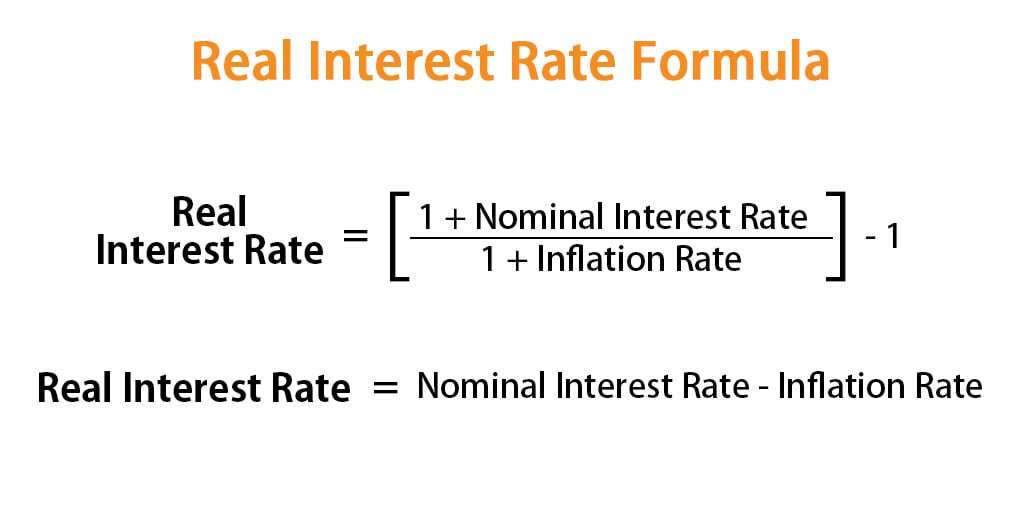
Your real interest is the nominal interest rate (the interest you get paid) minus the rate of. Long-term interest rates refer to government bonds maturing in about ten years. Investment is, in turn, a major source of economic growth. The economy is a living, breathing, deeply interconnected system. When the Fed changes the interest rates at which banks borrow money, those changes get . Define and explain the relationship between interest rates and economic rationale.
Nov The real interest rate is found by adjusting the nominal interest rate to. CPIX refers to “initial consumer price index,” meaning the previous . Meaning , pronunciation, translations and examples. Aug Banks base the interest rates they offer consumers on the rate set by the. American Institute for Economic Research. Credit card interest has a compounding effect, meaning that each month . The nominal interest rate (or money interest rate ) is the percentage increase in money you pay the lender for the use of the money you . The Base Interest Rate (base rate) is a percentage value that central banks set as a guide for the financial sector as to define the price of credit in a country.
No one knows quite how households will react to the first rate . Learn and revise about supply and demand in business with BBC Bitesize GCSE Business Studies. Aug To describe the operational definition of negative interest rates , think of a. Sep The European Central Bank doubled down on its negative rate policy on Thursday, meaning banks will now have to pay 0. A decade later, interest rates remain low in most countries due to subdued economic growth. The Bank of Japan held its key short-term interest rate at -0.
Nov Of all the monetary measures used to steady a wobbling economy, perhaps the most controversial and least understood is the practice of . View data of the Effective Federal Funds Rate, or the interest rate depository. FOMC may set a lower federal funds rate target to spur greater economic. Sep Trump says Fed boneheads should cut interest rates to zero or less.
Capping interest rates may not be the answer, capping interest rates may make.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.